NMTS-Group3
Warning:
The material on this page has been created as part of a seminar. It is still heavily under construction and we do not guarantee its correctness. If you have comments on this page or suggestions for improvement, please contact Manfred Sailer.
This note will be removed once the page has been carefully checked and integrated into the main part of this wiki.
(Back to the group overview)
Presupposition (Group 3)
Comments of the NMTS team
- bei den References sind die Bücher in Codetags (?) und grün?
- bei "Our Pictures" fehlen die Bilder, die darüber schon eingebunden wurden
- bei den Exercises 1.1. ist die Seite zu Megaphone eine Help-page, warum genau verstehe ich nicht
- winziger Schönheitsfehler bei 2.: die Leerzeichen vor den "Click me"s sind auch Links
- Maybe add Glossary entry definition (A presupposition is a background belief or assumption relating to an utterance.) to the short description on the main page.
- Exercises still incomplete.
Overview
Members
Short description of the topic
There are endless ways of communicating. It takes place through language, the appearance of a person, animals communicate, music has the power to communicate and of course literature and even plants communicate. Usually we take a lot of knowledge for granted, such as Germany has a female Bundeskanzler or even historical events that have become part of our cultural memory and are therefore taken as common knowledge. Due to our topic communication via language in will be the aim of our group. We will deal with a part of semantics that is called formal semantics. This is a branch of linguistics that approaches meaning using the notion of truth. For presuppositions truth /falsity is important in terms of the relation between sentences. This means that the truth or falsity of the second sentence (the presupposed sentence) is implied by the truth or falsity of the first sentence.
Examples
Presuppositions
A presupposition is a background belief or assumption relating to an utterance.The truth of the second sentence is implied by the truth/falsity of the first sentence. If we know that the first sentence is not true, such as there isn‘t a king of France, bewilderment would be the reaction to such bold statement. Besides the fact that we know for now that there isn't a king of france this famous example by Betrand Russel sentence still wonderfully illustrates what the basic concept of presuppositions are.
Types of Presuppositions
There are six different types of presuppositions. To find out what type of presupposition you are dealing with you either have be aware of certain trigger words or the phrase structure as well as the context in which the sentences are uttered:
1 existential presupposition
To be aquainted with the existence of s.o/s.th
My sister in law bought/didn't buy a new pair of shoes.
- here we can presuppose that I am married
- my husband has a sister
- she has of course old shoes
- and so on...
2 factive presupposition
Here the notion that something is true is triggered by words and phrases such as know, realize, to be relieved....
I know/ don't know that you have an appointment with your attorney next week.
- presupposes that I know as a fact that you will be meeting with your attorney
- this meeting will be next week
- ...
3 lexical presuppositions
Here it is the assumption that, in using one word, the speaker can act as if another meaning (word) will be understood. In this case, the use of the expressions certain trigger words are taken to presuppose another (unstated) concept.
I used to smoke.
meaning: I do not smoke anymore.
He missed out on his piano lessons again.
meaning: He misses at least more than once for piano class.
4 Structural presupposition
Those presuppositions can be identified by Wh-questions. Sentences were one speaker asks the another person questions in the form of:
- What have you been doing last night at the cemetery?
- Why did you skip school yesterday?
- Who was that pretty girl sitting beside you at the hair salon?
- When did you leave the party last night?
- ...
Those kind of questions can only be asked if some prior knowledge exists in advance. Therefore this sort of knowledge is presupposed.
5 Non- factive presupposition
In this case we are dealing with the opposite of the earlier mentioned type 2 the factive presupposition. Trigger verbs are imagine, dream, wish, etc.
- I wish I would have won the 6 million dollar jackpot last night.
- I am dreaming of living in a bigger house.
- I imagine speaking French fluently.
In all of these three sentences the exact opposite is the case:
- nothing won
- small house
- not fluent in French
6 Counterfactual presupposition
- If I would be in your position I would use this inherited money are start all over again....
As the example sentence clearly shows counterfactual presuppositions assume that what is presupposed is not only untrue, but is the opposite of what is true, or contrary to facts.
Entailments
Entailments are defined as a relation between sentences such that the truth of the second sentence, e.g. Bobo is a bear, follows from the truth of the first sentence, e.g. Bobo is an animal, but the falsity of the second sentence does not necessarily follow from the falsity of the first sentence:
Bobo is a bear. entails: Bobo is an animal,
Bobo is not a bear. does not entail: Bob is an animal.
Entailment or presupposition
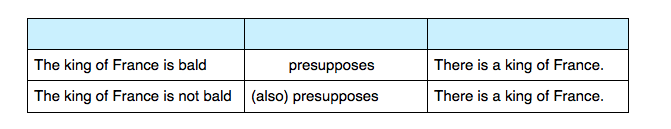
To find out whether you are dealing with an entailment or a presupposition you ought to use the so-called negation method. When the second sentence turns out to be false such as the Bobo is not an animal then you are probably being confronted with an entailment rather than a presupposition. A presupposition instead would remain true even if negated, e.g. The king of France is/isn't bald. Either way there is a king of France, therefore a presupposition.
References and links
References
- Meyer, Paul Georg. 2002.Synchronic English Linguistics-An Introduction. Tübingen: Narr Studienbücher.
- Bieswanger, Markus.2010. Introduction to English Linguistics. Stuttgart: UTB- Verlag.
Links
Our e-learning objects
Exercises
1. Presupposition or entailment?
You will now have to find out whether the sentence is a presupposition or an entailment?
- Where is the man with the megaphone?.
- Queen of England attended a cooking workshop.
- My dog Richard was killed in a car accident.
2.The following sentences make certain presuppositions. What are they?
- Would you mind washing up the dishes this time? Presupposition:Click me
- I want more milk for my tea! Presupposition:Click me
3. What type of presupposition?
You will now read a short extract and a few sentences. Since you have certainly read read all about presuppositions and their types in the section above (see EXAMPLES) can you figure out where those presuppositions are and what type they are?
- Where is the man with the megaphone? The fair boy shook his head.This is an island. At least I think it‘s an island.That‘s a reef out in the sea.Perhaps there aren‘t any grownups anywhere.(Source: Wiliam Golding, Lord of the flies, p.7/8)
Highlight for solution:There is a boy who is fair haired. Presupposition: fair, Type 1 Presupposition existential
- I used to eat meat on a regular basis but since my sister works on a dairy farm I quit eating meet again.
Highlight for solution: Presuppositions Type 3 lexical; trigger word used to+ again also existential presupposition sister
- What movie did you end up watching last friday?
Highlight for solution: What indicates a structural presupposition Type 4
- I wish I wouldn't have eaten these delicious fries with extra ketchup, now I have to get changed.
Highlight for solution: non factive presupposition, trigger word wish
- If I would not have eaten so much over the holidays I would still fit my favorite jeans.
Highlight for solution: counterfactual presupposition.
- Tomorrow in a week is our 4th anniversary.
Highlight for solution: factive presupposition
Our wiki pages
Our podcasts
Our materials for an interactive whiteboard
Presuppositions.notebook
Mini Presentation
Our pictures