NMTS-Group1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
=== Comments by the NMTS team === | === Comments by the NMTS team === | ||
* Short description: Only mentions lexical and structural ambiguity…. maybe add other types of ambiguity or say why you only talk about these two types. | * Short description: Only mentions lexical and structural ambiguity…. maybe add other types of ambiguity or say why you only talk about these two types. | ||
* | * glossary entry for "scope ambiguity" | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 31: | Line 20: | ||
=== Short description of the topic === | === Short description of the topic === | ||
Ambiguity is an extremely widespread phenomenon on which many puns and jokes are based on.<br/> | [[Glossary:Ambiguity#Ambiguity|Ambiguity]] is an extremely widespread phenomenon on which many puns and jokes are based on.<br/> | ||
It can be differentiated between lexical and structural ambiguity. [[Glossary:Lexical_Ambiguity|Lexical ambiguity]] is defined as words having multiple meanings. <br/> | It can be differentiated between lexical and structural ambiguity. [[Glossary:Lexical_Ambiguity|Lexical ambiguity]] is defined as words having multiple meanings. <br/> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 30: | ||
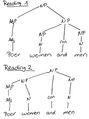
rich women and men: [rich women] and men ''or'' rich [women or men] <br/> | rich women and men: [rich women] and men ''or'' rich [women or men] <br/> | ||
Anna saw tourists with binoculars.: Anna saw [tourists with binoculars] ''or'' Anna saw [tourists] with binoculars. | Anna saw tourists with binoculars.: Anna saw [tourists with binoculars] ''or'' Anna saw [tourists] with binoculars. | ||
Besides these general terms, within the presentation and exercises more distinct terms are introduced: collective-distributive and scope.<br/> | |||
Collective-distributive ambiguity is defined on the level of morphemes. The ambigious parts of speech are the plural morphemes. <br/> | |||
''Example'': <br/> | |||
Mary and her sister had a little lamb: Mary and her sister own one little lamb together ''or'' each of them has an own little lamb.<br/> | |||
A double meaning is created on the lexical or structural level of meaning by: | A double meaning is created on the lexical or structural level of meaning by: | ||
| Line 53: | Line 47: | ||
*Kortmann, Bernd. 2005. ''English Linguistics: Essentials''. Berlin: Cornelsen Verlag. | *Kortmann, Bernd. 2005. ''English Linguistics: Essentials''. Berlin: Cornelsen Verlag. | ||
*Fromkin, Victoria; Rodman, Robert & Hyams, Nina. 2003. ''An Introduction to Language'' (7th edition). Boston: Thomson Heinle. | *Fromkin, Victoria; Rodman, Robert & Hyams, Nina. 2003. ''An Introduction to Language'' (7th edition). Boston: Thomson Heinle. | ||
*Matthias Bauer, Joachim Knape, Peter Koch, Susanne Winkler | *Matthias Bauer, Joachim Knape, Peter Koch, Susanne Winkler. 2010. Dimensionen der Ambiguität. Zeitschrift für Literaturwissenschaft und Linguistik 158, 7-75. | ||
=== Links === | === Links === | ||
| Line 66: | Line 60: | ||
* [[Glossary:Homonym|homonymy (definition in Basic Glossary)]] | * [[Glossary:Homonym|homonymy (definition in Basic Glossary)]] | ||
* [[Glossary:Scope_Ambiguity|Scope Ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)]] | |||
* [http://www2.let.uu.nl/Uil-OTS/Lexicon/ "ambiguity" in Utrecht Institute of Linguistics, Lexicon of Linguistics ] | * [http://www2.let.uu.nl/Uil-OTS/Lexicon/ "ambiguity" in Utrecht Institute of Linguistics, Lexicon of Linguistics ] | ||
| Line 77: | Line 73: | ||
== Our wikipages == | == Our wikipages == | ||
*[[Glossary:Ambiguity|Ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | |||
* [[Glossary:Antonym|antonym (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | * [[Glossary:Antonym|antonym (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | ||
* [[Glossary:entailment|entailment (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | * [[Glossary:entailment|entailment (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | ||
* [[Glossary:Homograph|homograph (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | * [[Glossary:Homograph|homograph (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | ||
* [[Glossary:Lexical_Ambiguity|Lexical Ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)]]<br/ > | |||
* [[Glossary:Polysemy|Polysemy (definition in Basic Glossary)]]<br/ > | |||
* [[Glossary:Register|register (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | * [[Glossary:Register|register (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | ||
* [[Glossary:Structural_Ambiguity|structural ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | * [[Glossary:Structural_Ambiguity|structural ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)]] <br/ > | ||
| Line 85: | Line 84: | ||
== Our podcasts == | == Our podcasts == | ||
<embedvideo service="youtube" dimensions="400">http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SyyqkS1aofI </embedvideo> | |||
[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SyyqkS1aofI Podcast on Lexical Ambiguity] | [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SyyqkS1aofI Podcast on Lexical Ambiguity] | ||
== Our materials for an interactive whiteboard == | |||
[http://user.uni-frankfurt.de/~sailer/nmts-wise1213/AmbiguityPresentation.notebook Notebook presentation] | |||
== Our pictures == | == Our pictures == | ||
| Line 101: | Line 100: | ||
File:PA080194.jpg|Jellyfishes (Zoo Berlin), Lorena's picture | File:PA080194.jpg|Jellyfishes (Zoo Berlin), Lorena's picture | ||
File:Leo.jpeg|Leo | File:Leo.jpeg|Leo | ||
File:Tree_Ambiguity.jpg|Poor women and men, Reading 1 & 2 | |||
File:Reading 1.png|Peter read the book on the Eiffel Tower, Reading 1 | |||
File:Reading 2.png|Peter read the book on the Eiffel Tower, Reading 2 | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Our exercises == | == Our exercises == | ||
=== Exercise I === | === Exercise I === | ||
| Line 144: | Line 142: | ||
''We need more intelligent administrators''.<br /> | ''We need more intelligent administrators''.<br /> | ||
→ [[Group1-Ex2-b-Solutions|Paraphrases]]<br /> | → [[Group1-Ex2-b-Solutions|Paraphrases]]<br /> | ||
c) Think of an ambiguous phrase or sentence on your own and explain its ambiguity.<br /> | c) Think of an ambiguous phrase or sentence on your own and explain its ambiguity.<br /> | ||
| Line 154: | Line 150: | ||
'''Trees'''<br /> | '''Trees'''<br /> | ||
a) Draw the two different trees of the following | a) Draw the two different trees of the following phrase.<br /> | ||
''poor women and men''<br /> | ''poor women and men''<br /> | ||
→ [[Group1-Ex2-c-Solutions|Trees]]<br /> | → [[Group1-Ex2-c-Solutions|Trees]]<br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:49, 3 April 2016
Warning:
The material on this page has been created as part of a seminar. It is still heavily under construction and we do not guarantee its correctness. If you have comments on this page or suggestions for improvement, please contact Manfred Sailer.
This note will be removed once the page has been carefully checked and integrated into the main part of this wiki.
(Back to the group overview)
Ambiguity (Group 1)
Comments by the NMTS team
- Short description: Only mentions lexical and structural ambiguity…. maybe add other types of ambiguity or say why you only talk about these two types.
- glossary entry for "scope ambiguity"
Overview
Members
Short description of the topic
Ambiguity is an extremely widespread phenomenon on which many puns and jokes are based on.
It can be differentiated between lexical and structural ambiguity. Lexical ambiguity is defined as words having multiple meanings.
Example:
Is life worth living? It depends on the liver.
Structural ambiguity arises when the syntactic structure of a sentence allows more than one meaning.
Example:
rich women and men: [rich women] and men or rich [women or men]
Anna saw tourists with binoculars.: Anna saw [tourists with binoculars] or Anna saw [tourists] with binoculars.
Besides these general terms, within the presentation and exercises more distinct terms are introduced: collective-distributive and scope.
Collective-distributive ambiguity is defined on the level of morphemes. The ambigious parts of speech are the plural morphemes.
Example:
Mary and her sister had a little lamb: Mary and her sister own one little lamb together or each of them has an own little lamb.
A double meaning is created on the lexical or structural level of meaning by:
References and links
References
- Bieswanger, Markus & Annette Becker. 2006. Introduction to English Linguistics (3rd edition). Tübingen and Basel: A. Francke Verlag.
- Kortmann, Bernd. 2005. English Linguistics: Essentials. Berlin: Cornelsen Verlag.
- Fromkin, Victoria; Rodman, Robert & Hyams, Nina. 2003. An Introduction to Language (7th edition). Boston: Thomson Heinle.
- Matthias Bauer, Joachim Knape, Peter Koch, Susanne Winkler. 2010. Dimensionen der Ambiguität. Zeitschrift für Literaturwissenschaft und Linguistik 158, 7-75.
Links
Our e-learning objects
Our wikipages
- Ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)
- antonym (definition in Basic Glossary)
- entailment (definition in Basic Glossary)
- homograph (definition in Basic Glossary)
- Lexical Ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)
- Polysemy (definition in Basic Glossary)
- register (definition in Basic Glossary)
- structural ambiguity (definition in Basic Glossary)
Our podcasts
Our materials for an interactive whiteboard
Our pictures
Our exercises
Exercise I
General definition of ambiguity
a) What is an ambiguous word?
1. a word with only one meaning
2. a polysemous word
3. a homophone word
b) What is the technical term for words that have more than one meaning?
1. scope ambiguity
2. lexical ambiguity
3. structural ambiguity
c) Which word is the ambiguous word in the sentence?
1. I bought it without any further inquiry.
2. There is no bank in this town.
d) Think of three sentences in which the word “hot” has different meanings.
Check your solution!
Exercise II
Different types of ambiguity
a) Phrases and sentences as a whole can have more than one meaning. How is this form of ambiguity called?
1. Scope Ambiguity
2. Lexical Ambiguity
3. Structural Ambiguity
b) Which two meanings does the following sentence contain? Paraphrase them.
We need more intelligent administrators.
→ Paraphrases
c) Think of an ambiguous phrase or sentence on your own and explain its ambiguity.
→ Example
Exercise III
Trees
a) Draw the two different trees of the following phrase.
poor women and men
→ Trees
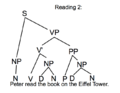
b) Draw the two different trees of the following sentence.
Peter read the book on the Eiffel-Tower.
→ Trees