SoSe15: Term paper project: Predicative and Attributive Adjectives: Difference between revisions
(→Task 2) |
(→Task 2) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | ||
Check your answer | Check your answer | ||
</div></div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
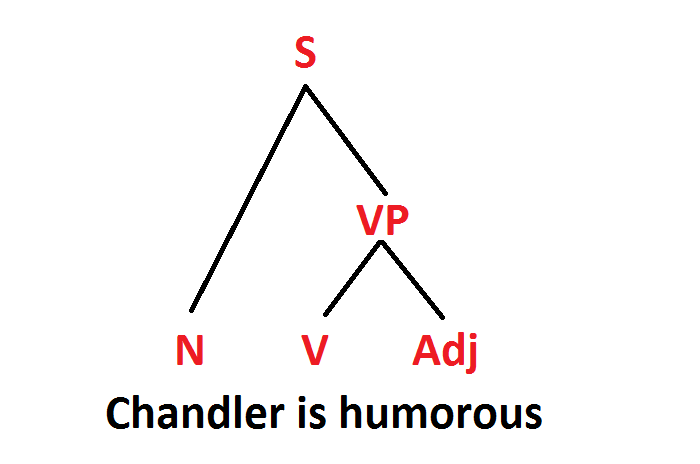
# Syntactic structure [[File:tree_1.png|options|caption]] | # Syntactic structure [[File:tree_1.png|options|caption]] | ||
| Line 54: | Line 55: | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 21:40, 29 July 2015
Warning:
The material on this page has been created as part of a seminar. It is still heavily under construction and we do not guarantee its correctness. If you have comments on this page or suggestions for improvement, please contact Manfred Sailer.
This note will be removed once the page has been carefully checked and integrated into the main part of this wiki.
Participants
- Ekram Aghdoube
- Hana Hashi
Short description of the project
Produced material
Task 1
Look at the following sentences and decide, whether the adjectives are used attributively or predicatively.
Task 2
Consider the following sentences.
- For each of these, provide the syntactic structure.
- Write down the logical forms.
- Provide a full analysis of the sentences, indicating following values: PHON, HEAD, PRED PLUS, ARG-ST, MOD, DR, INCONT, PARTS.
a. Chandler is humorous.
Check your answer
| | |humorous |- |PHON | < humorous > |- |HEAD | adjective |- |PRED | <plus> |- |ARG-ST | <NP[DR [c]] > |- |MOD | < > |- |DR | [a]chandler' |- |INCONT | <'[b]chandler' |- |PARTS | <humorous1, humorous1([a],[b]) > |- |}
b. The blonde waitress .
Check your answer
- Type of ambiguity: scope ambiguity
- Reading 1: every takes scope over a. Paraphrase: For every king there is at least one thane such that the king trusts that thane.
Reading 2: a takes scope over every. Paraphrase: There is one particular thane such that each king trusts this thane.
Back to the Semantics 2 page.